#Takeaways e-invoicing webinar 1: E-Invoicing beyond compliance
11 February 2025- Assess readiness by evaluating current systems, processes, and master data
- Make it a cross-departmental project
- Consider international expansion by aligning with future e-invoicing mandates.
E-Invoicing beyond compliance: a catalyst for Finance transformation
Compliance deadlines for mandatory e-invoicing across European markets are approaching fast. Many organizations aim at plain and simple regulatory adherence, yet e-invoicing presents opportunities beyond compliance. When approached strategically, e-invoicing can be a catalyst for broader Finance transformation, enhancing operational efficiency, improving cash flow, and strengthening vendor and customer relationships.
To support organizations in managing this shift, TriFinance is organizing a series of webinars on e-invoicing and Finance transformation, providing finance professionals with expert insights into regulatory changes and best practices.
In this article, we share key takeaways from the "E-Invoicing Beyond Compliance" webinar that was cast Monday, February 3, 2025. TriFinance experts Lander Coene, Project Consultant, and Ben Tuerlings, Project Manager, discussed the benefits of automation, integration with finance processes, and the role of e-invoicing in broader finance transformation initiatives. Vicky Posthumus, Expert Practice Lead Finance Transformation at TriFinance, hosted the session.
Understanding e-invoicing and EDI
E-invoicing is not a new concept—it is a form of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), allowing businesses to communicate through standardized, electronic formats instead of paper-based processes. PEPPOL (Pan-European Public Procurement OnLine) is actually a form of EDI. The evolution of PEPPOL has further standardized B2B invoicing, offering a secure, interoperable network for digital transactions.
EDI and Peppol differ in scope, cost, accessibility, and network structure:
- EDI supports a wide range of document types beyond invoicing, whereas Peppol focuses primarily on e-invoicing and procurement, though it is expanding.
- EDI is often complex and costly, while Peppol provides a standardized approach. EDI often relies on private networks, whereas Peppol is an open, standardized network , open network that is more accessible, particularly for smaller businesses.
- Additionally, EDI's two-corner model (Supplier & Customer) limits efficiency and scalability due to a lack of standardization, whereas the Peppol four-corner model (Supplier, AP Sender, AP Receiver, Customer) (ensures secure and uniform access across participants.
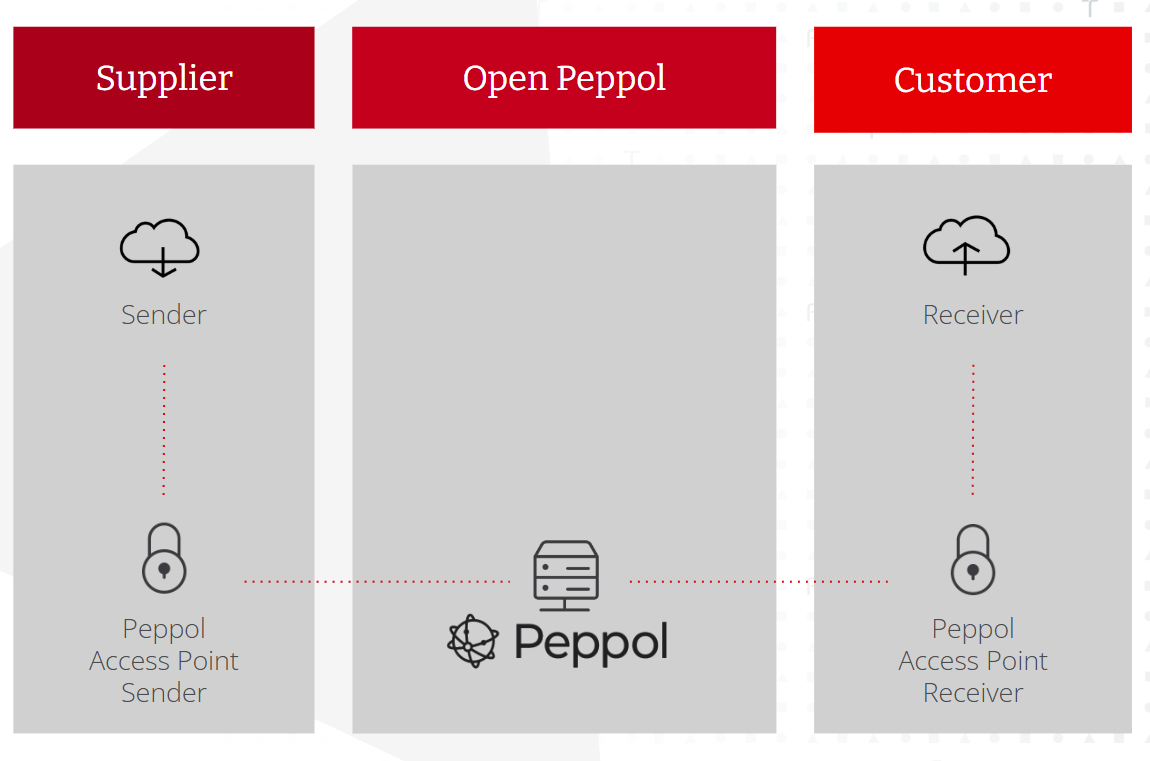
The 4-corner model in e-invoicing
An e-invoice is a data exchange between a supplier and a customer. It is not a pdf, but a structured XML-format. The 4-corner model is a framework for e-invoicing that enables secure, interoperable communication between parties on different networks.
In the 4-Corner Model, the main parties involved are:
- Corner 1: The Sender - Supplier/Service Provider that generates and sends the e-invoice.
- Corner 2: The Sender’s Access Point - The Sender’s Service Provider or access point responsible for sending the e-invoice on behalf of the sender. The access point translates the invoice into a standardized format ensuring it is sent securely.
- Corner 3: The Receiver’s Access Point - The access point that receives the e-invoice on behalf of the buyer (receiver). It translates the e-invoice into a format compatible with the receiver’s system.
- Corner 4: The Receiver (Buyer) - The recipient of the e-invoice, typically a buyer or client, who receives the invoice in a format ready for their internal processing.
Why e-invoicing?
The European Union introduced e-invoicing as part of its broader VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA) initiative, aiming to modernize tax reporting, combat fraud, and improve efficiency. One of the core elements of this initiative is the Digital Reporting Requirements (DRR), which will make e-invoicing mandatory for intra-EU B2B transactions by July 1, 2030. Additionally, ViDA seeks to simplify VAT rules, reducing the need for multiple VAT registrations across EU member states, and updating regulations for platform operators in sectors such as short-term rentals and passenger transport. These measures, set to take effect from July 1, 2027, are designed to create a more streamlined and transparent VAT system.
Another major driver for e-invoicing is the need to close the VAT gap—the difference between expected and collected VAT revenues. In Belgium alone, this gap is estimated at 7%, representing significant lost tax income due to fraud, evasion, and avoidance. By implementing e-invoicing, the EU aims to gain better oversight of VAT flows, ensuring that transactions are accurately reported and fraud risks are minimized.
Beyond tax compliance, e-invoicing plays a crucial role in reducing financial fraud. The digital nature of e-invoicing enables near real-time insights, which can help prevent fraudulent schemes such as VAT carousel fraud. It also addresses invoice fraud, where criminals intercept invoices and alter details, such as bank account numbers, to redirect payments.
Finally, e-invoicing serves as a catalyst for digital transformation within both public and private sectors. For governments, it simplifies VAT monitoring and enforcement, making tax administration more efficient. For businesses, the transition to e-invoicing brings several benefits, including cost savings through reduced paper usage and automated workflows, faster payments due to fewer processing errors, and improved auditability with standardized and traceable transact.
Key e-invoicing deadlines across Europe
Several EU member states are implementing e-invoicing requirements, each with varying deadlines. In Belgium, e-invoicing will be mandatory for B2B transactions by January 1, 2026. Germany has a phased rollout beginning January 1, 2025. In France, large and mid-sized businesses must issue e-invoices by September 1, 2026. Poland is rolling out a nationwide adoption through the KSeF platform, effective February 1, 2026.
E-Invoicing as a catalyst for transformation
With the upcoming e-invoicing mandate, organizations must decide how to implement this legal requirement. There are two main approaches: a technical, isolated implementation, and a broader transformation of the invoicing process.
A technical approach focuses solely on adding an e-invoicing access point to the existing system, ensuring compliance but offering limited long-term benefits.
On the other hand, a transformation approach considers the entire end-to-end invoicing process, including technology, processes, master data, and people, leading to broader operational improvements.
To implement e-invoicing effectively, organizations need to consider not only IT but also Finance, Purchasing, Sales, Legal, Tax, and Compliance. Additionally, external partners —such as key vendors and customers— should be involved early in the process to ensure smooth integration and prevent mismatched requirements. Overlooking these aspects can lead to disruptions in automated processes, such as missing critical data for management reporting.
A successful e-invoicing implementation starts with a clear understanding of current invoicing processes. Businesses should document and analyze their purchase-to-pay and order-to-cash workflows, identifying inefficiencies and redesigning them in alignment with the e-invoicing mandate. This ensures that the transition not only meets compliance but also enhances operational efficiency.
Benefits of e-invoicing for your organization
E-invoicing brings several tangible benefits across different business areas. In accounts payable, it eliminates manual processing and reduces errors associated with OCR tools. Automated invoice matching improves accuracy, freeing up resources for more value-added tasks. Faster processing enhances integration with accounting systems, reducing delays in financial reporting.
In treasury and cash flow management, system-to-system integration ensures invoices are received faster and more accurately. Late payments to vendors are minimized, reducing payment delays by up to 75%. The overall cash inflow improves as e-invoicing reduces Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) by an average of 10–20 days. Enhanced cash forecasting and real-time insights further strengthen financial planning and liquidity management.
For sales and procurement, e-invoicing significantly reduces manual efforts in generating invoices. It also prevents revenue leakage caused by missed charges or pricing errors. The integration of purchase-to-pay processes ensures that invoices are more accurate from the start, reducing the time spent on error corrections. Improved invoicing processes also lead to stronger vendor and customer relationships, boosting trust and collaboration while enhancing the company’s negotiation power.
From an organizational perspective, e-invoicing alleviates frustration among employees who previously dealt with invoice issues caused by manual input errors. Automation allows teams to focus on higher-value tasks, resulting in increased job satisfaction. Implementing e-invoicing with a global and future-proof strategy also accelerates market expansion, shortening time-to-market for new ventures.
Common pitfalls in e-invoicing implementation
- Treating e-invoicing as an IT-only project – Focusing solely on technical implementation can lead to missed business requirements and lost optimization opportunities. A holistic approach is crucial.
- Underestimating vendor and customer impact – If external stakeholders are unprepared or their requirements are not properly captured, issues like mismatched data and workflow disruptions will arise. Early collaboration is key.
- Poor master data governance – While cleaning up master data is a common first step, failing to maintain data quality can lead to errors and processing issues. Ongoing governance is essential.
- Neglecting change management – E-invoicing impacts multiple teams, increasing their workload. Without proper communication, training, and engagement, adoption will be slow, delaying the project’s success.
- Failing to scope the project correctly – Many projects run longer than expected due to an incomplete understanding of the full scope and impact. Identifying challenges early helps prevent delays and ensures timely delivery.
Conclusion
E-invoicing is no longer just a regulatory requirement—it is an opportunity for finance professionals to drive efficiency, enhance financial control, and future-proof their organizations. By treating e-invoicing as a strategic transformation, businesses can unlock significant value beyond mere compliance.
To successfully implement e-invoicing, organizations should:
- Make it a cross-departmental project involving finance, IT, procurement, and compliance teams.
- Consider international expansion by aligning with future e-invoicing mandates.
- Assess readiness by evaluating current systems, processes, and master data.
- Leverage transformation opportunities beyond compliance to optimize efficiency.
- Start early to ensure a smooth transition and avoid last-minute compliance challenges.
For more insights on Finance transformation, stay tuned for the upcoming webinars in our Finance Transformation Series.
E-Invoicing and Finance transformation
Webinar calendar and InsightsRelated content
-
Blog
Overcoming key hurdles in Finance Transformation: a guide for CFOs and Finance teams
-
Reference case
Contributing to finance transformation at VF Europe with temporary bookkeeping support
-
Reference case
Transforming Finance in EMEA for a specialty chemicals company
-
Blog
Improving efficiency and strategic alignment at an Investment Company
-
Blog
How to leverage AI in finance processes to improve forward-looking insights
-
Blog
Europe’s green deal turns pale
-
Career in Internal Team
Client Partner | Public Sector
-
Career as Consultant
Senior Finance consultant | Public sector
-
Career as Consultant
Junior Finance Consultant | Public Sector
-
Career as Consultant
Medior Finance Consultant | Public Sector
-
Career in Internal Team
Insurance expert manager
-
Career as Consultant
Young Graduate | Trainee Program