The total cost of implementing EPM
8 September 2024When it comes to managing your organization's performance, implementing an Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) tool can be a game-changer. A well-integrated EPM tool results in better planning and execution of your business strategy. Providing data analytics, reporting, budgeting and forecasting models, it allows you to assess your company’s performance, gain insights into your operations, and make informed, strategic decisions, all the while monitoring the entire process.
Like any major business investment, it is crucial to understand the costs involved and how they can be legitimated by an expected return on investment. In this article, we take a look at the cost structure of an EPM project, including associated costs, and how they impact your organization's bottom line, with a focus on optimizing your budget and maximizing ROI.
‘Calculating the cost of an EPM implementation is not a piece of cake,’ TriFinance Expert practice leader Data & Analytics Maarten Lauwaert says. ‘There are so many variables in an implementation that the total cost can only be estimated based on an organization’s specific requirements.’
Estimating EPM costs, including external and internal costs
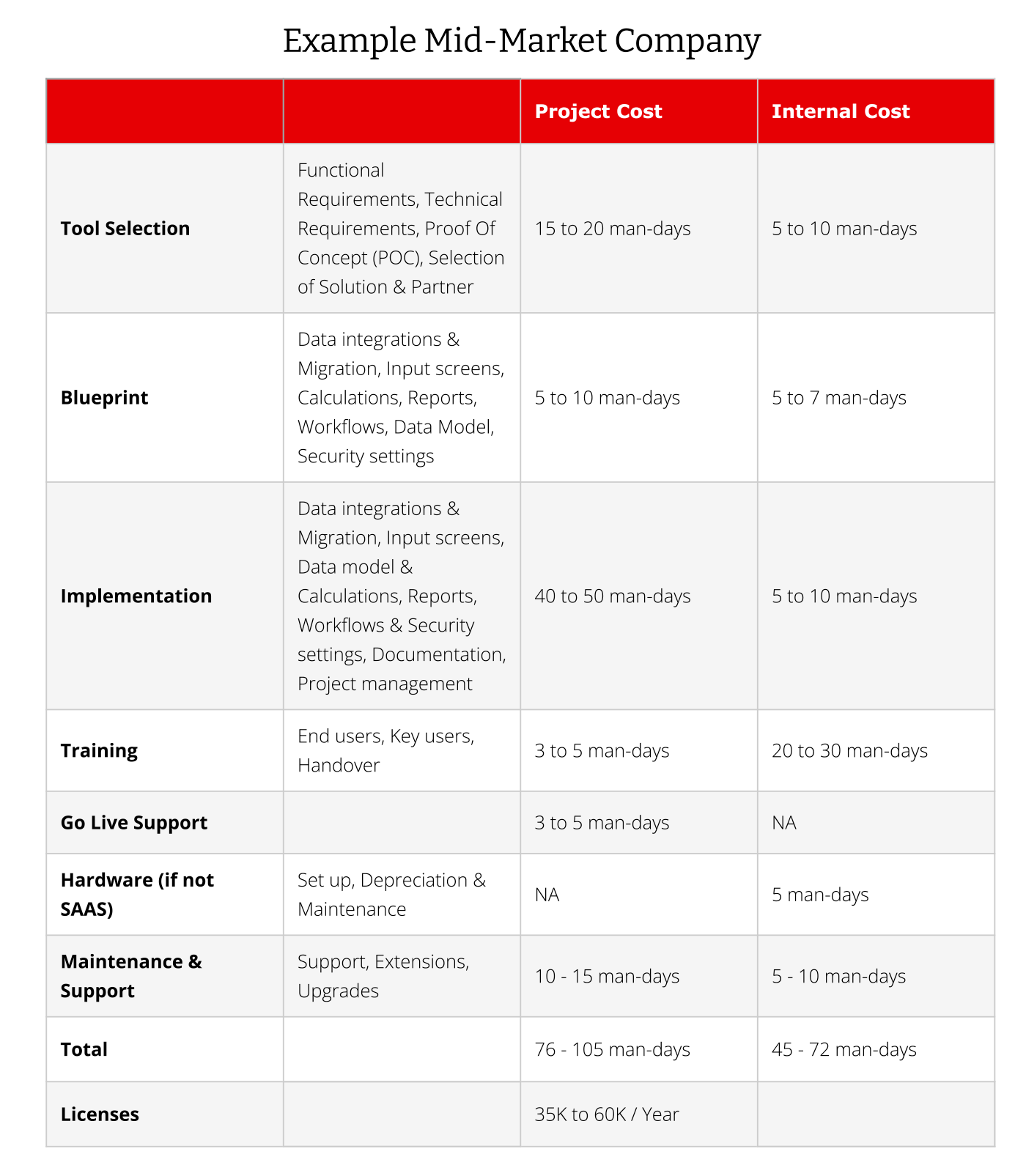
To estimate the cost of EPM, it is vital to consider the key stages of an implementation project such as tool selection, blueprint, implementation, training, go-live support, licenses, hardware, and maintenance & support. Each of these stages has an impact on the budget, overall financial planning and success of the EPM project.
For all of these stages, except the Go-Live Support and the License stages, costs can be divided into two main categories, related to external expertise and internal effort.
- External costs, primarily related to services provided by third parties that bring specialist knowledge and expertise to the project. These service providers play a crucial role in ensuring the successful deployment of the EPM software.
- Internal costs represent the time and effort invested by your organization's people. From the initial planning stages to post-implementation support, internal resources are essential for aligning the EPM tool with your specific business needs.
Cost drivers for a mid-market company
To facilitate the EPM cost calculation, we take the example of a mid-market company. Possible cost-drivers include the size and the complexity of the project, the processes that must be included, the user count, and the number of source systems.
Understanding these costs is vital for budget management. Properly planning your investment in EPM ensures that the implementation process stays on track and within budget, avoiding unnecessary expenditures.
Costing fundamentals: the stages of an EPM Implementation
To budget effectively for an EPM installation, start by identifying the primary cost drivers, which are crucial for evaluating the project's ROI. Analyzing these costs helps your organization optimize the budget, maximize ROI, and ensure your software aligns with your strategic objectives.
The implementation process of EPM software typically involves several phases:
1. Tool Selection: Selecting the right EPM tool is crucial for managing the cost and success of your implementation project. Start by ensuring the tool's functional and technical requirements align with your data strategy and organizational objectives.
Functional requirements include the features you need, such as consolidation, planning, forecasting, scenario analysis, ESG reporting, and/or IFRS reporting. The cost will vary based on the number of processes and whether you include transactional data.
Technical requirements involve determining the number of data sources to integrate, the user count, multi-language support, integration with your current data landscape, Single Sign-On, and security features.
Once you've clarified these requirements, you can document them in a blueprint or create a proof of concept. This will help to validate whether the solution will work under the requested conditions.
While selecting a new tool is often recommended, it isn’t always necessary. You may be able to build on an existing tool, which can streamline the process.
The selection process can take one to two months, depending on complexity and specific needs, and can influence overall costs.
2. Blueprint: Creating a blueprint before implementation is essential for tracking the process. Once the tool selection is complete, a big portion of the blueprint work is already done, allowing you to skip certain steps or minimize the work, which in turn can have a positive effect on the project cost.
When refining the blueprint for implementation, you should detail what will be built, including, for instance, the number and design of screens, and the specific logic tailored to the chosen application. While a blueprint helps ensure everyone has a clear understanding of the requirements and avoids potential risks during implementation, the number of man-hours for creating it is rather limited, as is its cost.
3. Implementation. During the implementation phase, data from various sources are integrated. This could involve loading data from flat files, building a data lake or data warehouse, or establishing a direct connection with your ERP system. These requirements should be clearly outlined in your blueprint, as they are essential to the implementation process.
Key questions to consider in this phase include how far back you need to go to retrieve historical data. ‘For an EPM implementation, I would always recommend setting up a data warehouse or data lake when integration is needed,’ Maarten Lauwaert says. ‘This allows you to use technology that minimizes the need for ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes. While many EPM tools offer direct connections to source systems, a data lake can streamline integration and reduce the need for ETL expertise.
Large data warehouse and data lake providers like Amazon, Microsoft and Google often have more advanced integration capabilities with source systems, which can be leveraged for your EPM project. While this work might be handled by teams outside your EPM tool, it will still impact the project budget. TriFinance, for example, integrates both BI and EPM software, allowing for seamless integration of these elements.
During the implementation, you will also need to address the development of input screens, calculations and dimensions in your data model. Decisions must be made on the structure of data reporting, the number of processes and workflows required, and the necessary documentation. Additionally, project management plays a key role throughout the process. Project costs also include internal expenses, primarily for requirements gathering, testing, and validation of data, models, and internal logic.
4. Training. Educating users on the new EPM tool is vital for a smooth transition. Once your EPM tool is implemented, it’s crucial to ensure that users are properly trained. Depending on the tool you’ve selected, you should plan for several hours of training for your team and other end users. The more users, the more training time you’ll need to allocate. The same goes for key users. Typically, you’ll need two to three key users for a small EPM project. For larger projects, you’ll need correspondingly more key users. For bigger projects, you should plan for one to two days to familiarize key users with the basic functionality.
The time required for the handover also depends on the project's size. During the handover, you’ll provide documentation that explains what has been built, not only in terms of functionality but also conceptually.
5. Go Live Support. At go-live, it is crucial to have support at hand to fix potential bugs or support the end users in their first steps in the new application.
6. Licenses. The cost of licenses varies greatly depending on the solution you have chosen, as well as on the number of users and the modules required. Some vendors charge per user, others use a combination of per-user pricing with a fixed fee, and some charge per module. While it’s difficult to provide exact figures, licensing costs for a cloud solution in a smaller project typically range from 35,000 to 60,000 euros on a yearly basis. For larger projects, these costs can be substantially higher.
7. Hardware. Although less relevant today, hardware costs still need to be considered. These include initial setup, depreciation, and maintenance. Nearly all new implementations are cloud-based solutions. Companies that purchased on-premise solutions and wish to expand their system’s functionality will probably continue to rely on their hardware.
Cloud solutions typically follow a user-based pricing model, which may be less cost-effective for companies with many users. In such cases, an on-premise model might be more economical, though it requires managing server hosting and maintenance.
8. Maintenance costs. Support for on-premise solutions is more intensive than for cloud solutions because you need to partially maintain the infrastructure. Cloud EPM software typically updates automatically, while on-premise solutions usually require updates every three to five years.
Maintenance needs also depend on changes to your model. How many extensions do you plan? Companies often expand their EPM tools because the technology intrinsically supports iterative growth, p.e. to other functional domains aa a.o. HR, operations, sales,….
Additionally, adopting an EPM tool can optimize processes beyond just speed and efficiency. While the improved quality and traceability provided by EPM are valuable, they are not easily quantified in financial terms.
Understanding the total cost of an EPM software implementation
The total cost of implementing an Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) tool is influenced by numerous factors, including tool selection, blueprint creation, integration, training, and ongoing support. Each phase of the implementation process brings its own set of costs, both external and internal, which can significantly impact your organization’s budget and overall success.
By thoroughly planning and accounting for these variables—from the selection of data sources and user training to the integration of existing systems—you can optimize your EPM investment and ensure that it delivers maximum value. Proper budgeting and strategic planning are essential to successfully navigating the complexities of EPM implementation and achieving a strong return on investment.
Contact us to discover how we can support you
Contact usRelated content
-
Blog
How the technology of Microsoft Fabric can help you maximize the value of your data
-
Article
How Lakehouse technology can help solve your siloed data problem
-
Blog
EFRAG’s simplified ESRS: what it means and why sustainability reporting still matters
-
Blog
Webinar takeaways: How to deal with common challenges in your data projects
-
Article
Why CFOs can’t afford to ignore Data Engineering in 2025
-
Article
Power BI training: from data literacy and data modeling to strategic reporting in finance